IT Crash Course Day 2: Networking Fundamentals & Operating Systems
Table of Contents
- Networking Fundamentals
- OSI Model and Network Protocols
- Windows Operating System Basics
- Linux Operating System Basics
- Network Security Basics
- Summary and Interview Preparation Tips
Networking Fundamentals
TCP/IP
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is the fundamental suite of protocols that powers the internet and most local networks.
Key Components:
- IP (Internet Protocol): Handles addressing and routing of packets
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): Ensures reliable, ordered delivery of data
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Provides faster, connectionless communication without guaranteed delivery
TCP/IP Model Layers:
- Network Interface Layer: Physical and data link functionality (Ethernet, Wi-Fi)
- Internet Layer: Addressing and routing (IP)
- Transport Layer: End-to-end communication (TCP/UDP)
- Application Layer: Network applications and services (HTTP, FTP, DNS)

Key Characteristics of TCP:
- Connection-oriented protocol
- Three-way handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK)
- Guarantees delivery and correct order
- Flow control and congestion management
- Used for: Web browsing, email, file transfers
Key Characteristics of UDP:
- Connectionless protocol
- No guarantee of delivery or order
- Lower overhead and latency
- Used for: Streaming media, VoIP, DNS queries
DNS
DNS (Domain Name System) translates human-readable domain names (like google.com) into machine-readable IP addresses (like 142.250.190.78).
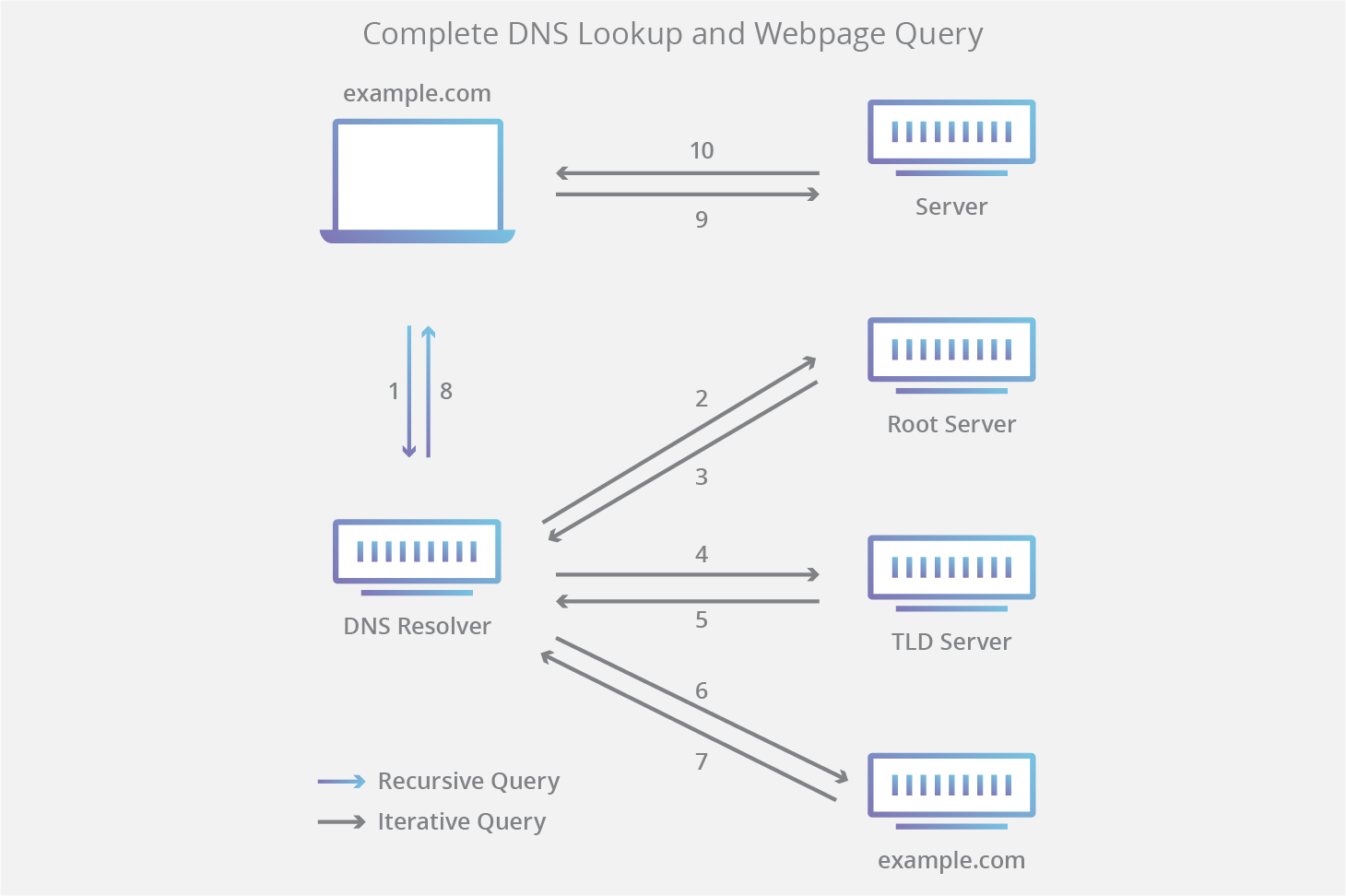
How DNS Works:
- User enters a URL in browser (www.example.com)
- Computer checks local DNS cache
- If not found, queries the configured DNS server
- DNS server either responds with the answer or forwards the request
- Once resolved, the IP address is returned and cached
- Browser connects to the IP address
DNS Record Types:
- A Record: Maps hostname to IPv4 address
- AAAA Record: Maps hostname to IPv6 address
- CNAME: Canonical name (alias) record
- MX: Mail exchange record
- NS: Nameserver record
- TXT: Text record (often used for verification)
DNS Hierarchy:
- Root DNS Servers (.)
- Top-Level Domain Servers (.com, .org, etc.)
- Authoritative DNS Servers (specific domains)
- Recursive DNS Resolvers (ISP or public DNS)
DHCP
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns IP addresses and network configuration to devices on a network.
DHCP Process (DORA):
- Discovery: Client broadcasts a request for an IP address
- Offer: DHCP server offers an IP address
- Request: Client requests the offered IP address
- Acknowledgment: Server confirms the address assignment

DHCP Configuration Information:
- IP address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway
- DNS servers
- Lease duration
- Other options (NTP servers, WINS servers, etc.)
DHCP Options:
- Static Assignment: Manual IP configuration
- Dynamic Assignment: Temporary automatic assignment
- Reservation: Consistent IP address based on MAC address
IP Addressing
IPv4 Addressing:
- 32-bit address (4 octets)
- Format: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx (each xxx is 0-255)
- Approximately 4.3 billion possible addresses
- Classes: A, B, C, D (multicast), E (experimental)
- Private ranges:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 (Class A)
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 (Class B)
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 (Class C)
IPv6 Addressing:
- 128-bit address (8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits)
- Format: xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx
- Approximately 340 undecillion (3.4×10^38) addresses
- Example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
- Can be shortened by removing leading zeros and replacing consecutive zero groups with ::
- Example shortened: 2001:db8:85a3::8a2e:370:7334
Subnetting Basics:
- Divides a large network into smaller networks
- Uses subnet mask to define network and host portions
- Common subnet masks:
- 255.0.0.0 (/8) - Class A
- 255.255.0.0 (/16) - Class B
- 255.255.255.0 (/24) - Class C

CIDR Notation:
- Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- Represented as IP address/prefix (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24)
- Prefix indicates number of bits in the network portion
- More flexible than traditional class-based addressing
Knowledge Check: Networking Fundamentals
-
Which protocol ensures reliable, ordered delivery of data packets? a) UDP b) ICMP c) TCP d) ARP
-
What does DNS primarily translate? a) IP addresses to MAC addresses b) Domain names to IP addresses c) Ports to services d) Protocols to applications
-
During which step of the DHCP process does a server offer an available IP address? a) Discovery b) Offer c) Request d) Acknowledgment
-
Which of the following is a private IPv4 address range? a) 8.8.8.0/24 b) 127.0.0.0/8 c) 192.168.0.0/16 d) 203.0.113.0/24
-
In CIDR notation, what does the "/24" in 192.168.1.0/24 represent? a) The number of available IP addresses b) The number of subnet bits c) The number of network bits d) The number of host bits
OSI Model and Network Protocols
The 7 Layers of OSI
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes network communication functions into seven distinct layers.
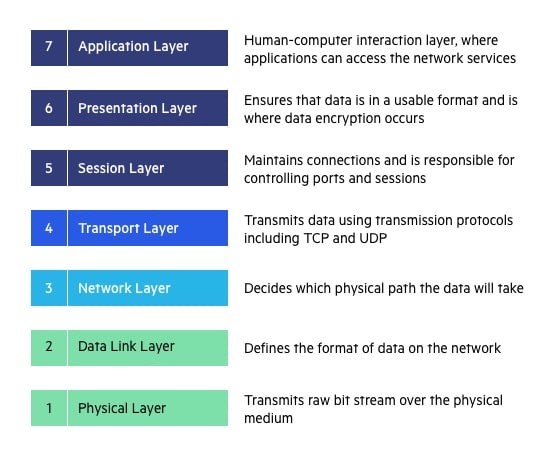
Layer 7: Application Layer
- Function: Interface between network and applications
- Examples: HTTP, SMTP, FTP, DNS
- Key Concepts: Application protocols, user interfaces
- Devices: Endpoints, application firewalls
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
- Function: Data translation, encryption, compression
- Examples: SSL/TLS, JPEG, MPEG
- Key Concepts: Data format conversion, encryption/decryption
- Processes: Encoding, compression, encryption
Layer 5: Session Layer
- Function: Establishes, maintains, and terminates connections
- Examples: NetBIOS, RPC, SOCKS
- Key Concepts: Session establishment, session maintenance
- Processes: Dialog control, synchronization
Layer 4: Transport Layer
- Function: End-to-end communication, segmentation
- Examples: TCP, UDP
- Key Concepts: Connection management, error control, flow control
- Devices: Load balancers
Layer 3: Network Layer
- Function: Routing, logical addressing
- Examples: IP, ICMP, OSPF
- Key Concepts: Packet forwarding, addressing, routing
- Devices: Routers, Layer 3 switches
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
- Function: Physical addressing, error detection
- Examples: Ethernet, PPP, ARP
- Key Concepts: Frames, MAC addresses, error checking
- Devices: Switches, bridges
Layer 1: Physical Layer
- Function: Transmission of raw bits over physical medium
- Examples: Ethernet cables, fiber optics, wireless signals
- Key Concepts: Bit transmission, physical topology
- Devices: Hubs, repeaters, cables
Common Network Protocols
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: Web page retrieval and display
- Port: 80
- Characteristics: Stateless, text-based
- Key Components: Request methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
HTTPS (HTTP Secure)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7) with Presentation (Layer 6) security
- Purpose: Secure web communications
- Port: 443
- Security: TLS/SSL encryption
- Benefits: Data integrity, authentication, encryption
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: File transfers between client and server
- Ports: 20 (data), 21 (control)
- Characteristics: Separate control and data connections
- Security: Basic authentication, FTPS adds encryption
SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: Secure file transfers
- Port: 22
- Security: SSH encryption
- Advantage: More secure than standard FTP
SMB (Server Message Block)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: File and printer sharing on Windows networks
- Ports: 445 (modern versions)
- Features: File sharing, printer sharing, named pipes
- Versions: SMBv1, SMBv2, SMBv3 (progressively more secure)
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: Remote desktop access to Windows systems
- Port: 3389
- Features: Graphics transmission, encryption, authentication
- Security: Network Level Authentication (NLA)
SSH (Secure Shell)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: Secure remote administration
- Port: 22
- Features: Encrypted terminal access, secure file transfers
- Common Uses: Server management, tunneling
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: Email sending
- Port: 25 (unencrypted), 587 (with STARTTLS)
- Characteristics: Text-based commands
- Security: Often enhanced with TLS
IMAP/POP3 (Email Retrieval)
- OSI Layer: Application (Layer 7)
- Purpose: Email retrieval
- Ports: 143/993 (IMAP), 110/995 (POP3)
- Differences: IMAP maintains email on server, POP3 typically downloads
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
- OSI Layer: Network (Layer 3)
- Purpose: Network diagnostics and error reporting
- Examples: Ping, Traceroute
- Characteristics: No ports, uses type and code numbers
Knowledge Check: OSI Model and Protocols
-
Which layer of the OSI model handles logical addressing and routing? a) Layer 2 (Data Link) b) Layer 3 (Network) c) Layer 4 (Transport) d) Layer 5 (Session)
-
Which protocol would be most appropriate for securely transferring files between servers? a) FTP b) HTTP c) SFTP d) SMTP
-
What is the primary difference between HTTP and HTTPS? a) HTTPS uses port 443 while HTTP uses port 80 b) HTTPS encrypts data in transit while HTTP does not c) HTTPS is faster than HTTP d) HTTP supports more request methods than HTTPS
-
Which protocol is commonly used for Windows file sharing? a) FTP b) SSH c) SMB d) IMAP
-
At which OSI layer does TCP operate? a) Layer 3 (Network) b) Layer 4 (Transport) c) Layer 5 (Session) d) Layer 6 (Presentation)
Windows Operating System Basics
Essential Command-Line Interface
CMD (Command Prompt) vs PowerShell:
- CMD: Traditional command interpreter in Windows
- PowerShell: More powerful scripting environment with object-oriented approach
Essential Networking Commands:
ipconfig
- Purpose: Display IP configuration information
- Common Options:
ipconfig /all: Detailed configurationipconfig /release: Release DHCP leaseipconfig /renew: Request new DHCP leaseipconfig /flushdns: Clear DNS cache
C:\> ipconfig /all
Windows IP Configuration
Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . : DESKTOP-PC
Primary DNS Suffix . . . . . . :
Node Type . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP Routing Enabled. . . . . . . : No
WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . : No
Ethernet adapter Ethernet:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Description . . . . . . . . . . . : Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 00-11-22-33-44-55
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.100
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
ping
- Purpose: Test network connectivity
- Usage:
ping hostnameorping IP_address - Options:
-t: Continuous ping-n count: Specify number of echo requests-l size: Specify buffer size
C:\> ping google.com
Pinging google.com [142.250.190.78] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 142.250.190.78: bytes=32 time=15ms TTL=57
Reply from 142.250.190.78: bytes=32 time=14ms TTL=57
Reply from 142.250.190.78: bytes=32 time=14ms TTL=57
Reply from 142.250.190.78: bytes=32 time=15ms TTL=57
Ping statistics for 142.250.190.78:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 14ms, Maximum = 15ms, Average = 14ms
tracert
- Purpose: Trace route to destination
- Usage:
tracert hostnameortracert IP_address - Function: Shows path and latency to destination
C:\> tracert google.com
Tracing route to google.com [142.250.190.78]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 1 ms 1 ms 1 ms 192.168.1.1
2 8 ms 7 ms 7 ms 10.0.0.1
3 10 ms 9 ms 9 ms 172.16.1.1
4 15 ms 14 ms 14 ms core1.provider.net
5 15 ms 14 ms 15 ms 142.250.190.78
Trace complete.
netstat
- Purpose: Display network connections
- Common Options:
-a: Display all connections and listening ports-n: Display addresses in numerical form-b: Display executable involved in connection (requires admin)-o: Display process ID
C:\> netstat -an
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:3389 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 127.0.0.1:6463 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 192.168.1.100:54268 142.250.190.78:443 ESTABLISHED
nslookup
- Purpose: Query DNS records
- Usage:
nslookup domain_name - Function: Resolves host names to IP addresses
C:\> nslookup microsoft.com
Server: dns.google
Address: 8.8.8.8
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: microsoft.com
Addresses: 2620:1ec:c11::200
20.112.52.29
Other Essential Commands:
- systeminfo: Display system configuration information
- tasklist: Display running processes
- taskkill: Terminate processes
- sfc /scannow: System File Checker to repair Windows files
- chkdsk: Check disk for errors
File Systems
NTFS (New Technology File System)
- Primary Windows file system
- Key Features:
- File and folder permissions
- Encryption (EFS)
- Compression
- Disk quotas
- File system journaling
- Support for large volumes (up to 256 TB theoretically)
- Use Cases: System drives, data drives requiring security
FAT32 (File Allocation Table)
- Older file system
- Limitations:
- 4GB maximum file size
- 32GB maximum partition size (effectively)
- No built-in security features
- Advantages:
- Wide compatibility (cameras, older devices)
- Use Cases: USB drives, cross-platform compatibility
exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table)
- Modern FAT-based file system
- Features:
- Large file size support (up to 16 exabytes)
- No practical volume size limit
- Better than FAT32 for flash drives
- No security features like NTFS
- Use Cases: External drives, cross-platform storage
Comparison Table:
| Feature | NTFS | FAT32 | exFAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max File Size | 16TB | 4GB | 16EB |
| Max Volume Size | 256TB | 32GB | 128PB |
| Security | Yes | No | No |
| Journaling | Yes | No | No |
| Compatibility | Windows (limited on macOS/Linux) | Universal | Good cross-platform |
| Recommended Use | Windows system drives | Small flash drives, legacy devices | Large external drives |
User and Group Management
User Account Types:
- Local Administrator: Full control over the local computer
- Standard User: Limited privileges, can run most applications
- Guest: Highly restricted (typically disabled by default)
User Management Tools:
- Computer Management Console:
compmgmt.msc - User Accounts in Control Panel
- Local Users and Groups MMC snap-in:
lusrmgr.msc - Command-line:
net usercommands

Common User Management Tasks:
- Create user:
net user username password /add - Delete user:
net user username /delete - Change password:
net user username newpassword - Add to group:
net localgroup groupname username /add
Important Windows Groups:
- Administrators: Full control over the computer
- Users: Standard user permissions
- Remote Desktop Users: Can connect via RDP
- Backup Operators: Can back up files and directories
- Power Users: More privileges than standard users (legacy)
Security Identifiers (SIDs):
- Unique identifiers for user accounts and groups
- Format: S-1-5-21-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxx
- Used for access control instead of names
- Can be viewed with
whoami /usercommand
Event Viewer
Purpose: Central location for Windows system, security, and application logs
Accessing Event Viewer:
- Type
eventvwr.mscin Run dialog or search - Administrative Tools > Event Viewer
- PowerShell:
Get-EventLogcmdlet

Main Log Categories:
- Application: Events recorded by applications
- Security: Security audit events (logons, privilege use)
- System: OS component events
- Setup: OS upgrade and installation events
- Forwarded Events: Events from other computers
Event Severity Levels:
- Information: Normal operation events
- Warning: Potential issues that might need attention
- Error: Significant problems that didn't prevent operation
- Critical: Severe errors causing system/application failures
- Audit Success/Failure: Security events
Using Event Viewer for Troubleshooting:
- Filter events by time period around issue occurrence
- Look for Error or Critical events
- Note Event IDs and sources
- Research specific Event IDs online
- Check for patterns or related events
Common Event IDs to Know:
- 4624: Successful logon
- 4625: Failed logon attempt
- 7036: Service started or stopped
- 41: System rebooted without clean shutdown
- 1074: System shutdown initiated
Knowledge Check: Windows OS Basics
-
Which command would you use to view detailed network configuration information? a) netstat -a b) ipconfig /all c) ping localhost d) tracert 127.0.0.1
-
What is the primary advantage of NTFS over FAT32? a) Better compatibility with older devices b) Faster read/write speeds c) File and folder level permissions d) Smaller cluster sizes
-
Which tool would you use to investigate application crashes on a Windows system? a) Task Manager b) Event Viewer c) Resource Monitor d) System Configuration
-
What does the following command do?
net localgroup Administrators username /adda) Creates a new user called "username" b) Adds an existing user to the Administrators group c) Creates a new group called "Administrators" d) Removes a user from the Administrators group -
In Windows Event Viewer, which log would contain information about failed login attempts? a) Application log b) System log c) Security log d) Setup log
Linux Operating System Basics
Linux Distributions
Linux Distribution (Distro): Complete Linux operating system package including the kernel, utilities, applications, and package management system.
Major Distribution Families:
Debian-based:
- Ubuntu: User-friendly, popular for desktops and servers
- Debian: Stable, focuses on free software
- Mint: Beginner-friendly desktop environment
- Package Management: APT (apt-get, apt)
Red Hat-based:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL): Commercial, enterprise-focused
- CentOS/Rocky Linux: Free enterprise-grade distros
- Fedora: Cutting-edge features, Red Hat testing ground
- Package Management: YUM/DNF
SUSE-based:
- SUSE Linux Enterprise: Commercial enterprise distro
- openSUSE: Community version for developers and enthusiasts
- Package Management: Zypper
Arch-based:
- Arch Linux: Rolling release, minimalist approach
- Manjaro: User-friendly Arch derivative
- Package Management: Pacman
Other Notable Distributions:
- Gentoo: Source-based distribution for advanced users
- Slackware: One of the oldest distributions, minimal
- Kali Linux: Security and penetration testing
Basic Command-Line Navigation
Terminal Access:
- GUI: Terminal application
- Text mode: Ctrl+Alt+F1 to F6
- Remote: SSH client
Basic Navigation Commands:
pwd (Print Working Directory)
- Purpose: Shows current directory
- Example:
pwd→/home/username/documents
ls (List)
- Purpose: List directory contents
- Common Options:
ls -l: Long format with detailsls -a: Show hidden filesls -h: Human-readable file sizes
- Example:
ls -la→ Show all files with details
$ ls -la
total 48
drwxr-xr-x 3 user group 4096 May 10 12:34 .
drwxr-xr-x 24 user group 4096 May 10 12:30 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 user group 220 May 10 12:32 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 user group 3771 May 10 12:32 .bashrc
drwxr-xr-x 2 user group 4096 May 10 12:34 documents
-rwxr-xr-x 1 user group 15340 May 10 12:33 script.sh
cd (Change Directory)
- Purpose: Navigate between directories
- Common Usages:
cd directory: Move to specified directorycd ..: Move up one directorycd ~: Move to home directorycd /: Move to root directorycd -: Move to previous directory
mkdir (Make Directory)
- Purpose: Create new directories
- Example:
mkdir new_folder - Options:
mkdir -p parent/child/grandchild(create parent directories if needed)
rm (Remove)
- Purpose: Delete files and directories
- CAUTION: Deletions are permanent, no recycle bin
- Options:
rm file.txt: Delete a filerm -r directory: Delete directory and contents recursivelyrm -f file.txt: Force deletion without prompting
cp (Copy)
- Purpose: Copy files and directories
- Examples:
cp file.txt destination/cp -r directory/ destination/(copy directory recursively)
mv (Move)
- Purpose: Move/rename files and directories
- Examples:
mv file.txt destination/mv file.txt newname.txt(rename)
cat (Concatenate)
- Purpose: Display file contents
- Example:
cat filename.txt
Finding Help:
man command: Display manual pagecommand --help: Brief help informationinfo command: Detailed documentation
File Permissions
Linux Permission Model: Three types of users:
- Owner: The user who owns the file
- Group: Users belonging to the file's group
- Others: All other users
Three types of permissions:
- Read (r): View file contents or list directory contents
- Write (w): Modify file or create/delete files in directory
- Execute (x): Run file as program or access directory
Permission Display:
-rwxr-xr--
│└┬┘└┬┘└┬┘
│ │ │ └── Others permissions (r--)
│ │ └───── Group permissions (r-x)
│ └──────── Owner permissions (rwx)
└────────── File type (- for regular file, d for directory)
Common Permission Patterns:
755 (rwxr-xr-x): Common for executables and directories644 (rw-r--r--): Common for regular files600 (rw-------): Private files777 (rwxrwxrwx): Full access to everyone (security risk)
Changing Permissions:
chmod(Change Mode):- Symbolic:
chmod u+x file(add execute to user) - Numeric:
chmod 755 file(rwxr-xr-x)
- Symbolic:
Numeric Permission Calculation:
- Read (r) = 4
- Write (w) = 2
- Execute (x) = 1
- Add values for each permission set:
- rwx = 4+2+1 = 7
- r-x = 4+0+1 = 5
- r-- = 4+0+0 = 4
Changing Ownership:
chown(Change Owner):chown user:group filechown -R user:group directory(recursive)
Special Permissions:
- Set User ID (SUID): Run file with owner permissions
- Set Group ID (SGID): Run file with group permissions
- Sticky Bit: Only owner can delete files in directory
Knowledge Check: Linux OS Basics
-
Which of the following is NOT a Debian-based Linux distribution? a) Ubuntu b) Mint c) Fedora d) Debian
-
What command would you use to create a new directory called "backup" inside your home directory? a)
cd ~/backupb)mkdir ~/backupc)touch ~/backupd)ls ~/backup -
In the Linux permission model, what does the permission string "rwxr-x---" represent? a) Owner can read/write/execute, group can read/execute, others have no permissions b) Owner can read/write, group can execute, others can read c) Owner can read/execute, group can read/write, others can execute d) All users can read/write/execute
-
What is the numeric value for the permission string "rw-r-----"? a) 740 b) 640 c) 460 d) 604
-
Which command would you use to view the contents of a file named "log.txt"? a)
view log.txtb)open log.txtc)cat log.txtd)read log.txt
Network Security Basics
Firewalls
Firewall Definition: Security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Types of Firewalls:
- Packet Filtering: Examines packets and allows/denies based on rules
- Stateful Inspection: Tracks active connections and makes decisions
- Application Layer: Examines application-specific data
- Next-Generation Firewalls: Combines traditional firewall with additional features
Windows Firewall:
- Built-in Windows security feature
- Controls inbound and outbound connections
- Maintains separate profiles for different network types
Windows Firewall Components:
- Profiles: Domain, Private, Public
- Inbound Rules: Control incoming connections
- Outbound Rules: Control outgoing connections
- Connection Security Rules: IPsec rules

Managing Windows Firewall:
- Basic Interface: Control Panel > Windows Defender Firewall
- Advanced Interface: Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security
- Command Line:
netsh advfirewallcommands - PowerShell:
Get-NetFirewallRule,New-NetFirewallRule
Common Firewall Rules:
- Allow/block specific applications
- Allow/block specific ports
- Allow/block specific IP addresses or ranges
- Configure rules by protocol (TCP/UDP)
Best Practices:
- Use default-deny approach
- Only open necessary ports
- Regularly review firewall rules
- Test firewall configuration
- Document all rule changes
Antivirus/Anti-malware
Malware Types:
- Virus: Self-replicates by attaching to programs
- Worm: Self-replicates independently
- Trojan: Disguised as legitimate software
- Ransomware: Encrypts data for ransom
- Spyware: Collects information without consent
- Adware: Displays unwanted advertisements
- Rootkit: Provides privileged access to a system
Anti-malware Protection Layers:
- Real-time Scanning: Monitors system activity constantly
- On-demand Scanning: Manual or scheduled scans
- Behavior Monitoring: Detects suspicious behaviors
- Heuristic Analysis: Identifies unknown threats
- Cloud-based Detection: Uses online databases
Windows Security (Windows Defender):
- Built-in security solution for Windows
- Real-time protection
- Periodic scanning
- Cloud-delivered protection
- Tamper protection
- Controlled folder access

Third-party Security Solutions:
- Offer additional features beyond basic protection
- Examples: Norton, McAfee, Bitdefender, Kaspersky
- May include additional tools like VPN, password manager
Best Practices:
- Keep antivirus always enabled and updated
- Perform regular full system scans
- Update operating system and applications
- Use multiple security layers
- Be cautious with email attachments and downloads
Password Hygiene and Security Practices
Password Best Practices:
- Use long passwords (12+ characters)
- Combine uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols
- Avoid using personal information
- Use different passwords for different accounts
- Change passwords periodically
- Consider using passphrases
Password Manager Benefits:
- Generates strong, unique passwords
- Securely stores passwords
- Auto-fills credentials
- Available across devices
- Examples: LastPass, Bitwarden, 1Password
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- Something you know (password)
- Something you have (phone, token)
- Something you are (biometric)
- Significantly increases security
General Security Practices:
- Keep software updated
- Use encryption when available
- Be cautious with public Wi-Fi
- Enable automatic updates
- Regularly backup important data
- Use secure browsing habits
Social Engineering Awareness:
- Be suspicious of unsolicited emails or calls
- Verify identities before providing information
- Don't click on unknown links
- Be careful with social media information
- When in doubt, verify through official channels
Physical Security:
- Lock devices when not in use
- Use screen protectors for privacy
- Secure devices in public places
- Consider cable locks for laptops
- Implement clean desk policy
Knowledge Check: Network Security
-
What is the primary function of a firewall? a) Scan files for viruses b) Control network traffic based on security rules c) Encrypt data transmitted over the network d) Detect intrusion attempts
-
Which Windows Firewall profile would typically be active when connecting to a public Wi-Fi hotspot? a) Domain profile b) Private profile c) Public profile d) Guest profile
-
Which type of malware encrypts user files and demands payment for the decryption key? a) Spyware b) Rootkit c) Worm d) Ransomware
-
What is a major advantage of using a password manager? a) It makes all your accounts use the same password b) It allows you to use simpler passwords c) It generates and stores unique passwords for different accounts d) It eliminates the need for passwords completely
-
Which of the following is an example of multi-factor authentication? a) Using a complex password with special characters b) Entering a password and a code from your phone c) Changing your password every 30 days d) Using different passwords for different accounts
Summary and Interview Preparation Tips
Key Concepts Review
Networking Fundamentals:
- TCP/IP is the foundation of internet communication
- DNS translates domain names to IP addresses
- DHCP automates network configuration
- IP addressing includes IPv4 and IPv6 with subnetting
OSI Model:
- 7 layers from Physical to Application
- Each layer has specific functions and protocols
- Common protocols operate at specific layers
Windows OS:
- Command-line tools for networking diagnostics
- File systems with different features and use cases
- User and group management for security
- Event Viewer for troubleshooting
Linux OS:
- Various distributions for different purposes
- Basic command-line navigation
- File permissions control access to resources
Network Security:
- Firewalls control network traffic
- Antivirus/anti-malware protects against threats
- Good password practices are essential
Interview Preparation Tips
Technical Knowledge:
- Review and understand all concepts in this guide
- Practice explaining complex concepts simply
- Be prepared to discuss real-world applications
Hands-On Practice:
- Use command-line tools regularly
- Set up a virtual lab for experimentation
- Troubleshoot common scenarios
Scenario Preparation:
- "How would you troubleshoot a network connectivity issue?"
- "Explain the process of setting up a secure user account."
- "What steps would you take to protect a computer from malware?"
Communication Skills:
- Practice explaining technical concepts to non-technical people
- Use analogies to simplify complex ideas
- Show logical thought processes when solving problems
Questions to Ask the Interviewer:
- "What tools does your team use for network monitoring?"
- "How does the team handle security incidents?"
- "What kind of troubleshooting scenarios are most common?"
Remember that IT support roles require both technical knowledge and soft skills like communication, problem-solving, and customer service. Be prepared to demonstrate both during interviews.
Good luck with your IT career journey!

